Thinking about a list of things to do before opening a restaurant? You’re about to enter an industry with over 1 million restaurant businesses in the United States alone. It’s an exciting journey, but one that demands careful planning and preparation.
Opening a restaurant requires significant upfront capital for space, equipment, permits, staffing, and marketing. Furthermore, the average restaurant profit margin typically hovers between just 3-5%, making proper preparation critical for success. According to a 2021 Restaurant & Catering report, food quality is the major factor contributing to success, followed by service quality and meeting customer expectations.
We’ve created this comprehensive guide to help you navigate the challenging landscape of starting a restaurant business. Despite the fact that the restaurant employee turnover rate is nearly 80% and only 34% of restaurant employees have employer-provided health insurance, a well-crafted restaurant business plan can become your roadmap to success. From securing finances to choosing the perfect location, we’ll walk you through the essential steps to open your restaurant in 2025 with confidence.
Define Your Restaurant Concept
A restaurant concept forms the foundation of your business identity when opening a restaurant. This crucial element defines everything from menu choices to atmosphere, guiding all aspects of your establishment’s personality and operations.
What is a restaurant concept?
A restaurant concept encompasses the overall idea or theme that defines your establishment. Essentially, it’s the unique identity and personality that sets your restaurant apart from competitors. Your concept includes several key elements:
- Menu design and food style
- Service approach
- Dining room decor and ambiance
- Overall customer experience
- Brand personality
The concept extends beyond just serving food—it tells a story through your dishes and represents the cultures they signify. When well-executed, your restaurant concept becomes the heart and soul of your establishment, shaping every decision from paint colors to plate presentations.
Why your concept matters
Having a clearly defined restaurant concept is vital for several reasons when starting a restaurant business:
First, it helps you stand out in a saturated market. The stark lines that once divided traditional restaurant concepts have been replaced by overlapping categories, making differentiation crucial. A unique concept creates an unforgettable experience that makes customers feel special and eager to return.
Additionally, a strong concept helps define your target audience. Whether you’re catering to families, young professionals, or food enthusiasts, your concept should align with their preferences. This targeted approach significantly increases your chances of success.
Moreover, a well-defined concept ensures consistency across all aspects of your business, building trust and loyalty among customers. This consistency makes marketing easier by providing a clear message to communicate.
How to define your restaurant concept
Creating your restaurant concept involves several intentional steps:
Initially, find inspiration from your heritage, local ingredients, travel experiences, or personal interests. The most authentic concepts often emerge from a chef’s personal experiences or passions.
Next, add a unique spin that differentiates your restaurant from competitors. Consider what will excite customers and create buzz around your new establishment.
Subsequently, research your customer base thoroughly. Understanding the demographics and dining preferences of locals helps ensure demand for what you plan to offer. Analyze competition and observe where other businesses have found success.
Then, develop a menu that reflects your theme without becoming muddled or confusing. Your menu should align with customer expectations while offering something distinctive.
Finally, choose a service style that complements your food offerings. Whether it’s family-style Italian dining or fine dining for seafood entrees, your service approach should enhance the overall concept.
Remember, the success of your restaurant hinges on this concept—it’s what attracts customers, earns positive reviews, and builds a loyal following.
Write a Restaurant Business Plan
Creating a detailed roadmap is crucial in your list of things to do before opening a restaurant. Once you’ve defined your concept, putting it into a formal business plan transforms your culinary dream into an actionable strategy.
What is a restaurant business plan?
A restaurant business plan serves as the blueprint that outlines your entire vision, explaining in detail how your new business will take shape and operate once the doors open. This document describes your restaurant’s goals and the steps you’ll take to make those goals a reality. It includes your financial projections, background information, and organizational strategies that govern day-to-day restaurant activities.
Think of your business plan as the north star guiding your restaurant journey. Whether you’re at the initial concept stage or ready to secure funding and partners, this plan keeps you focused on what matters.
Why it matters for starting a restaurant business
Your restaurant business plan plays several critical roles in your venture’s success:
- Secures potential investors – Opening a restaurant typically requires outside capital from investors or silent partners who need to see concrete plans before investing
- Provides operational guidance – When dealing with construction, licensing, staffing, and other operational challenges, your business plan acts as a roadmap
- Demonstrates thorough planning – Shows investors you’ve considered every expense and scenario, providing a complete roadmap to success
- Clarifies direction – Helps translate general strategies into actionable plans for reaching specific goals
Indeed, without a solid business plan, obtaining funding becomes extremely difficult—sometimes impossible. Even if funding isn’t your primary concern, this document provides clear direction on implementing your restaurant vision.
How to write a restaurant business plan
Creating an effective restaurant business plan requires several key components:
- Executive Summary – Introduce and summarize your vision, including mission statement, concept, execution plan, potential costs, and anticipated return on investment
- Company Overview – Explain ownership structure, location, restaurant type, and customer experience vision
- Industry Analysis – Describe market conditions, competition, and your unique niche
- Target Market – Define your ideal customers and how they compare to the industry demographics
- Competitive Analysis – Detail existing restaurants in your area, particularly those with similar concepts
- Marketing Strategy – Outline your promotion plans before and after opening
- Operations Plan – Describe staffing, service policies, systems, and suppliers
- Financial Analysis – Include investment plans, projected profit and loss statements, break-even analysis, and expected cash flow
Obviously, starting with a template designed for restaurants can make this process more manageable. Many industry-specific templates contain all the essential sections you’ll need to create a compelling business plan.
Remember that your business plan doesn’t just help you secure funding—it becomes your constant reference point throughout the restaurant opening process, helping you navigate challenges and stay focused on your vision.
Plan Your Restaurant Finances
Securing proper financing is the lifeblood of your new restaurant venture. Restaurant finance management involves obtaining and managing funds to sustain operations and generate profit for owners. With average profit margins between just 3-5%, understanding the financial aspects becomes even more critical.

Key considerations for funding
Restaurant funding options vary based on your business scale and concept:
Bank loans – Traditional term loans ranging from Rs. 20 lakhs to Rs. 3 crores with interest rates typically between 12% and 20%
Government programs – Schemes like PMEGP or MUDRA loans offer support for small restaurant ventures
Angel investors – Particularly those interested in food and beverage concepts
Working capital loans – Provide short-term financing for operational needs
Lenders typically require a personal credit score of 750 or above, along with experience in the hospitality sector. Consequently, maintaining a strong credit profile through timely repayments is essential.
Common funding mistakes
First-time restaurateurs often focus solely on securing startup capital rather than considering working capital needs until breaking even. Typically, underestimating startup costs leads to failure in raising adequate funds.
Another critical mistake is overestimating revenue in financial projections. This can lead to overspending on inventory, staffing, or marketing. Rather than being overly optimistic, base your forecasts on conservative trends and data.
Many owners also fail to budget for marketing, which is an investment in your business growth. Of course, your marketing budget is essential for generating buzz and filling seats.
Expert tips for budgeting
Create detailed budgets that account for operating expenses, tax obligations, and unexpected costs. Regularly compare your projections with actual performance every month to catch issues early, such as rising food costs or unnecessary labor hours.
Set aside a contingency fund that can cover three to six months of operating expenses. This financial safety net can cover unexpected expenses like broken equipment or bridge slow periods.
Track important ratios such as food cost percentage and labor cost ratio to optimize every dollar spent. Aim for a labor-to-revenue ratio of 25%-30% where possible.
Cost implications of undercapitalization
Undercapitalization occurs when a business doesn’t have enough cash to maintain operations and pay creditors. A restaurant that is profitable “on paper” can still be undercapitalized in practice.
The consequences include inability to weather negative changes in cash flow, which significantly increases the risk of insolvency. Similarly, undercapitalized restaurants lack flexibility to invest in growth opportunities, upgrade equipment, or respond to market changes.
To avoid this fate, develop a budget aligned with your business plan and regularly monitor deviations. Additionally, set up credit lines in advance so agreements are in place and capital is standing by when needed.
Choose the Right Location
Selecting the perfect location stands as a make-or-break decision on your list of things to do before opening a restaurant. After all, even exceptional food and service cannot overcome the limitations of a poor location.

What makes a good restaurant location?
A good restaurant location combines several critical elements. First, high visibility ensures your establishment catches the attention of potential customers and stays top-of-mind when dining decisions are made. Importantly, a prominent location with proper signage functions as constant advertising to passersby.
Accessibility represents another crucial factor. Convenient parking and simple access make your restaurant more appealing compared to competitors with challenging entry points. Specifically, adequate parking spaces and uncomplicated traffic patterns prevent dining out from becoming a stressful experience for patrons.
The demographic profile of the surrounding area must align with your concept and price point. Naturally, opening an upscale restaurant in a predominantly student area would create a mismatch between offering and audience.
Why location impacts success
Location directly determines your restaurant’s upper limit of success. The convenience of transportation reflects accessibility, with higher accessibility meaning higher potential customer demand.
The financial impact is significant—your location influences:
- Operating costs and profitability
- Marketing expenses required to attract customers
- Overall revenue potential
As a practical example, in one trade area, the local population might spend INR 4219.02 million annually on restaurants with about 10 competitors, whereas another area might see INR 16876.09 million in spending but with over 50 restaurants competing. This demonstrates how the competitive landscape affects your market share.
How to choose the right location
Begin by thoroughly researching your target market and identifying areas where they live, work, and spend leisure time. Visit potential locations at different times of day and week to evaluate traffic patterns and neighborhood activity.
Consider safety and crime rates in the neighborhood, as unsafe areas will deter both customers and staff. Furthermore, ensure the location complies with zoning regulations and health department requirements.
For different restaurant types, location needs vary:
- Quick-service restaurants thrive on high foot traffic and spontaneous visits, making busy areas essential despite higher rent
- Casual dining benefits from accessibility near universities or tourist attractions
- Fine dining performs well in upscale neighborhoods or business districts with high-income professionals
Remember that rent should never exceed 10% of your expected revenues. Nonetheless, don’t sacrifice quality merely for lower rent—a good location often justifies the additional cost through increased customer volume.
Design Your Restaurant Layout

A well-designed restaurant layout forms the backbone of your operational success and must be prioritized when opening a restaurant. The physical arrangement of your space impacts everything from customer experience to staff efficiency.
“Focus on a patron and employee restaurant design first, one that hums during slow and slammed shifts, then fill your space with the best, most cost-effective, most profitable food and beverage menus second. Menus can be easily tweaked. Finished construction, not so much”
Hanson Li, Restaurateur and investor, founder of Salt Partners Group
What is restaurant layout planning?
Restaurant layout planning involves creating a map of your restaurant’s physical space that includes all essential elements of your establishment. This blueprint encompasses the dining area, waiting space, kitchen, prep areas, storage, bathrooms, and how these components fit together.
In most cases, you’ll need to include this layout in your application for a business permit. The floor plan serves as a visualization tool showing how your restaurant will look and function once built. First-time restaurant owners often underestimate the importance of this step in the preparation process.
Why layout affects operations
The layout of your restaurant directly impacts both employee workflow and guest experiences—as well as your overall efficiency and profitability. A well-planned layout creates a seamless flow for customers from the moment they enter until they leave, enhancing their dining experience.
For customers, a thoughtful layout means easy navigation throughout the space, comfortable seating, and an enjoyable atmosphere. For staff, it means removing obstacles to perform their jobs quickly and efficiently. A playful and efficient layout leads to faster service, happier customers, and potentially bigger tips for your staff.
Additionally, a strategic layout can improve your restaurant’s revenue. Research shows that the way a restaurant is designed directly impacts how much money it makes. When customers can easily navigate your establishment, they’re more likely to explore the menu and discover additional items they want to try.
How to design your restaurant layout
To design an effective restaurant layout:
- Balance your space allocation – The dining room should occupy about 60% of your total space, with kitchen and preparation areas taking up the remaining 40%.
- Consider customer flow – Create clear pathways throughout your restaurant to prevent bottlenecks and congestion.
- Plan for different zones – Embrace the power of zones for different activities from entrance to bar to dining area.
- Utilize design software – Programs like SmartDraw, ConceptDraw, or CadPro can help create customized floor plans.
- Prioritize accessibility – Ensure your layout complies with building codes and is accessible to all guests.
Above all, remember that the layout must align with your restaurant’s concept and theme. Different restaurant formats require different designs—quick-service restaurants aim for fast eating and quick table turnover, whereas fine dining establishments seat customers for longer periods.
Obtain Licenses and Permits
Navigating the regulatory maze is a crucial step on your list of things to do before opening a restaurant. Legitimate operation requires multiple government approvals, with most restaurants needing 12 to 16 different licenses before opening their doors.
What licenses are needed to open a restaurant?
The “core eight” licenses appear consistently across most jurisdictions:
- FSSAI License – The most important license authorizing you to run a food business, issued by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India
- Health/Trade License – Issued by municipal corporations to ensure compliance with sanitation and hygiene norms
- Eating House License – Mandatory permit for public restaurants, obtained from the Licensing Police Commissioner
- Fire Safety NOC – Certifies compliance with fire safety regulations
- Shop and Establishment License – Regulates working conditions, wages, and employee policies
- GST Registration – Required for collecting taxes and claiming input credits
- Liquor License – Necessary if you plan to serve alcoholic beverages
- Environmental Clearance – Ensures your restaurant causes no pollution
Additional licenses might include signage permits, music licensing, and lift clearance depending on your operations.
Why permits are critical
Operating without valid licenses exposes you to significant risks. Many states impose penalties ranging from INR 42,190 to INR 2,531,413 for operating without proper documentation. Beyond fines, enforcement officers may immediately shut down your establishment if key approvals are missing.
Furthermore, these licenses protect public health by ensuring your restaurant meets specific hygiene, food handling, and safety standards. With average restaurant profit margins between 5-10%, even a single five-figure fine can eliminate months of income.
How to obtain restaurant licenses
Begin by creating a comprehensive checklist of local, state, and federal requirements 90-120 days before your planned opening. Prioritize long-lead items like liquor licenses or fire department permits, as these often involve background checks or public hearings.
For the FSSAI license, apply through their official portal (FoSCoS) by completing Form B, submitting required documents, and paying the applicable fee. The inspection typically takes one week to one month depending on documentation.
Likewise, apply for your Health/Trade License through your state’s Municipal Corporation website or Citizen’s Service Bureau. The fire safety NOC should be submitted to your state fire department, usually through their online portal.
Remember to allocate sufficient budget for licensing fees, which often exceed INR 84,380 combined. Even with perfect timing, anticipate a 2-3 month approval process before your restaurant can legally open.
Develop Your Menu
Your menu serves as the primary sales tool when opening a restaurant business. In fact, customers spend approximately 109 seconds reviewing their options, making your menu design a critical component of your success.
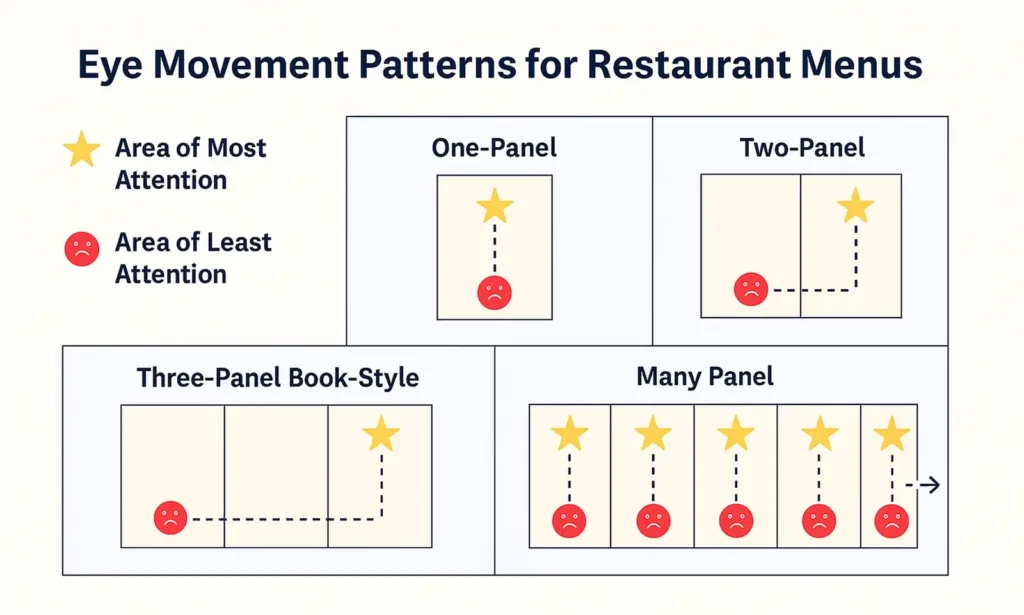
What goes into a restaurant menu?
An effective restaurant menu combines strategic organization, thoughtful design, and persuasive content. The foundation includes:
- Clear categories following a logical progression
- Strategic item placement in the “golden triangle” (top right, top left, center)
- Readable typography and thoughtful color schemes
- Descriptive language that evokes sensory experiences
- Strategic pricing presentation (often without currency symbols)
The most successful menus aren’t just lists of dishes but subtle guides that influence purchasing decisions. Throughout the design process, consider how visual elements like white space, font styles, and strategic placement can boost average order values by up to 30%.
Why your menu defines your brand
Your menu communicates your restaurant’s personality, style, and values at a glance. The fonts you select convey mood—elegant serif fonts suggest fine dining, while playful sans-serifs indicate casual experiences. Menu design directly affects revenue generation and patron morale.
Beyond esthetics, your menu establishes expectations about food quality, pricing, and overall experience. Hence, maintaining consistency between your menu design and other branding elements creates trust and reinforces your identity.
How to create a profitable menu
Menu engineering—analyzing both profitability and popularity—forms the cornerstone of menu development. Categorize items into four groups:
- Stars: High profit/high popularity – Keep prominent
- Plowhorses: Low profit/high popularity – Adjust ingredients or pricing
- Puzzles: High profit/low popularity – Improve placement or descriptions
- Dogs: Low profit/low popularity – Remove or rework completely
For maximum profitability, track key metrics like food cost percentage and contribution margin. The formula is simple: Contribution margin = Sales revenue – Variable costs.
Remember that effective menus are never static. Regular analysis and adjustment based on performance data helps maintain profitability while satisfying changing customer preferences.
Purchase Equipment and Supplies
The proper selection of kitchen equipment stands as a critical investment on your list of things to do before opening a restaurant. Quality equipment enables smooth operations, enhances food quality, and ensures cost savings throughout your restaurant journey.
What equipment is needed to open a restaurant?
Essential restaurant equipment includes:
- Cooking Equipment: Commercial ovens, ranges, griddles, and deep fryers
- Food Prep Equipment: Mixers, slicers, and food processors for reduced labor time
- Refrigeration: Walk-in coolers, reach-in refrigerators (₹50,000-₹1,00,000), and freezers (₹75,000-₹1,50,000)
- Storage & Organization: Shelving units, racks, and food containers to maximize kitchen space
- Sinks & Washing: Compartment sinks, handwashing stations, and dishwashing equipment
- Technology: POS systems and Kitchen Display Systems (KDS) for streamlined order management
Why equipment choices matter
Undoubtedly, the right equipment directly impacts operational efficiency. Quality commercial equipment offers durability, minimizing downtime from repairs. Meanwhile, energy-efficient appliances reduce utility bills without compromising food safety.
How to purchase restaurant equipment
Consider these purchasing approaches:
- Local Supply Stores: Offers guidance from sales representatives
- Online Retailers: Convenient for those who know exactly what they need
- Secondhand Equipment: Can save money on high-cost items
Naturally, prioritize high-quality equipment for core items used heavily, especially your main stove or fryer.
Hire and Train Your Staff
Your restaurant team represents the heart of your business operations. Without properly hired and trained staff, even the best restaurant concept will struggle to succeed.
“Although a great restaurant experience must include great food, a bad restaurant experience can be achieved through bad service alone. Ideally, service is invisible. You notice it only when something goes wrong”
Dana Spiotta, Award-winning novelist and essayist, known for commentary on American culture
What roles to hire for
Practically every restaurant needs five core staffing categories:
- Managerial staff – General managers and assistant managers
- Kitchen staff – Executive chef, sous chef, line cooks
- Floor staff – Servers, hosts, and bussers
- Bartenders – For establishments serving alcohol
- Delivery staff – If offering takeout services
Why staff training is crucial
Primarily, effective training enhances operational efficiency and consistency across shifts. Restaurants with structured training programs experience 23% higher profit per employee. Yet, the industry struggles with approximately 75% employee turnover rates.
Training produces tangible benefits:
- Enhanced customer experiences
- Increased staff confidence
- Improved food safety compliance
- Lower turnover costs
How to build a great restaurant team
First, create a comprehensive training manual covering procedures, responsibilities and expectations. Simultaneously, establish fair workloads based on each employee’s talents and aptitudes.
For retention, offer competitive salaries plus development opportunities—94% of employees stay longer at companies investing in their career growth. Create open communication channels where staff feel heard and valued.
Market and Launch Your Restaurant
Effective marketing stands as the final critical step on your list of things to do before opening a restaurant. With over 1 million restaurant locations nationwide competing for attention, a strategic marketing plan becomes your lifeline to success.
What is restaurant marketing?
Restaurant marketing involves the strategic planning and execution of activities that promote your establishment’s products, services, and brand to your target audience. It encompasses various tactics designed to attract and retain customers while establishing a distinct identity in a crowded market. Remarkably, nearly 90% of customers research restaurants online before booking, making your digital presence particularly important.
Why marketing drives traffic
In essence, marketing helps restaurants win more business by showcasing their services and building brand recognition. Without effective marketing, consumers won’t know what your restaurant offers, regardless of how exceptional your concept might be. A detailed marketing campaign helps your restaurant reach wider audiences, build reputation, and increase revenue. Marketing also allows you to target specific demographic groups that align with your restaurant’s concept.
How to launch your restaurant successfully
To launch successfully:
- Create a user-friendly website featuring your menu, high-quality images, and reservation options
- Optimize your site for search engines using relevant keywords
- Develop engaging content showcasing your restaurant’s personality
- Partner with local food bloggers and influencers to expand your reach
- Gather customer information for email marketing campaigns
Interestingly, hiring a part-time social media manager can be a smart investment when attracting new customers.
Comparison Table
| Step | Key Components | Importance/Impact | Implementation Tips | Common Challenges |
| Define Restaurant Concept | • Menu design & food style • Service approach • Dining room decor • Brand personality | Creates unique identity and shapes all business decisions | • Find inspiration from heritage/experiences • Add unique differentiators • Research customer base • Develop aligned menu | Standing out in saturated market |
| Write Business Plan | • Executive Summary • Company Overview • Industry Analysis • Financial Projections | • Secures investors • Provides operational guidance • Demonstrates planning | • Use industry-specific templates • Include all essential sections • Focus on clear direction | Translating vision into actionable plans |
| Plan Finances | • Bank loans • Government programs • Angel investors • Working capital | Critical with 3-5% average profit margins | • Create detailed budgets • Set contingency fund • Track important ratios | Underestimating startup costs and working capital needs |
| Choose Location | • Visibility • Accessibility • Demographics • Parking | Directly determines success ceiling | • Research target market areas • Visit at different times • Consider safety/regulations | Finding balance between rent costs and potential revenue |
| Design Layout | • Dining area (60%) • Kitchen (40%) • Customer flow • Zones | Impacts efficiency and profitability | • Use design software • Prioritize accessibility • Align with concept | Creating efficient workflow while maintaining ambiance |
| Obtain Licenses | • FSSAI License • Health License • Fire Safety NOC • GST Registration | Legal requirement with heavy penalties | • Start 90-120 days before opening • Prioritize long-lead items | Long approval processes and multiple requirements |
| Develop Menu | • Strategic organization • Item placement • Pricing strategy • Visual design | Influences purchasing decisions | • Use menu engineering • Track metrics • Regular analysis | Balancing profitability with popularity |
| Purchase Equipment | • Cooking equipment • Food prep tools • Refrigeration • Technology | Enables smooth operations | • Prioritize quality for core items • Consider energy efficiency • Compare purchase options | High initial investment costs |
| Hire & Train Staff | • Managerial staff • Kitchen staff • Floor staff • Support roles | Critical for customer experience | • Create training manual • Establish fair workloads • Offer development opportunities | High turnover rates (75%) |
| Market & Launch | • Website development • SEO optimization • Social media • Local partnerships | Essential for customer acquisition | • Create engaging content • Partner with influencers • Gather customer data | Standing out in competitive market |
Conclusion
Starting a restaurant takes courage, planning, and dedication. Throughout this guide, we’ve walked through the essential steps to transform your culinary dream into a thriving business by 2025. Undoubtedly, success in the restaurant industry depends on meticulous preparation across multiple fronts.
Your restaurant concept serves as the foundation upon which everything else builds. This unique identity will guide your decisions from menu creation to interior design. After establishing your concept, a comprehensive business plan becomes your roadmap, helping secure funding and providing operational guidance through each phase of development.
Financial planning deserves special attention considering the industry’s tight 3-5% profit margins. A well-structured budget with contingency funds protects your business from unexpected challenges that might otherwise derail your venture.
Location and layout decisions significantly impact your restaurant’s ceiling for success. The perfect location balances visibility, accessibility, and alignment with your target demographic, while an efficient layout enhances both customer experience and operational flow.
Regulatory compliance through proper licensing prevents costly penalties and closures. Similarly, strategic menu development using menu engineering principles helps maximize profitability while delighting customers.
Quality equipment and well-trained staff form the operational backbone of your restaurant. Though equipment represents a substantial upfront investment, durability and efficiency pay dividends over time. Likewise, investing in proper staff training reduces turnover costs and elevates customer experiences.
Finally, effective marketing ensures your target audience discovers your restaurant. Without strategic promotion, even the most exceptional dining experience remains unknown.
The restaurant industry certainly presents challenges, yet armed with this comprehensive guide, you’re well-positioned to join the ranks of successful restaurateurs. Remember that thorough planning now prevents costly mistakes later.
We encourage you to revisit this guide as you progress through each stage of opening your restaurant. Though the journey may seem daunting, the reward of seeing your restaurant concept come to life makes every step worthwhile. Best wishes as you embark on this exciting culinary adventure!
Key Takeaways
Opening a restaurant in 2025 requires strategic planning across ten critical areas, from concept development to marketing launch. Here are the essential insights every aspiring restaurateur needs:
• Define a unique restaurant concept first – Your concept shapes every decision from menu to decor and helps you stand out in a saturated market with over 1 million restaurants competing.
• Secure adequate funding with contingency planning – With average profit margins of just 3-5%, budget for 3-6 months of operating expenses beyond startup costs to avoid undercapitalization.
• Location determines your success ceiling – Choose high-visibility, accessible locations that align with your target demographic, even if rent is higher, as good locations justify costs through increased volume.
• Obtain all licenses 90-120 days before opening – Most restaurants need 12-16 different permits, with penalties ranging from ₹42,190 to ₹25,31,413 for non-compliance.
• Invest in staff training to reduce 75% industry turnover – Restaurants with structured training programs experience 23% higher profit per employee and significantly lower replacement costs.
Remember that 90% of customers research restaurants online before visiting, making your digital marketing strategy as crucial as your food quality. Success comes from executing each step methodically rather than rushing to open.
FAQs
Q1. How much does it typically cost to open a restaurant?
The cost to open a restaurant can vary widely, but generally ranges from $275,000 to $425,000. This includes expenses for leasing space, purchasing equipment, obtaining licenses, initial inventory, and working capital for the first few months of operation.
Q2. What are the most important factors to consider when choosing a restaurant location?
Key factors include visibility, accessibility, parking availability, local demographics, competition, and alignment with your restaurant concept. The location should have high foot traffic, be easily accessible to your target customers, and comply with local zoning regulations.
Q3. How long does it usually take to open a restaurant from concept to launch?
On average, it takes about 6 to 12 months to open a restaurant from initial concept to grand opening. This timeline can vary depending on factors such as location selection, renovation needs, licensing processes, and staff hiring and training.
Q4. What are the essential licenses and permits needed to open a restaurant?
The core licenses typically include a food service license, health permit, business license, certificate of occupancy, and liquor license (if applicable). Additional permits may be required depending on your location and specific operations.
Q5. How can I make my restaurant stand out in a competitive market?
To stand out, focus on developing a unique concept, creating a memorable dining experience, offering exceptional food quality and service, implementing effective marketing strategies, and building a strong online presence. Engaging with the local community and consistently gathering and acting on customer feedback can also help differentiate your restaurant.